Optimized Lubrication Management
Optimized Lubrication Management
Keywords: Lubrication, Maintenance management
Abstract:
Somebody said, the operation of some mechanical plant is riding on the thinnest oil slick which related to the energy saving, life circle of equipment, quality of products, safety and even the environment protection. However, lubrication is always taken as to oil the machine by many operators.
Establishing optimized lubrication management is urgently needed and belongs to an important part of maintenance management.
In this paper the authors give a framework of the system. The first issue of an optimized lubrication management is to establish an effective organization structure of lubrication management. The second important one is the choice of lubricant. The core of optimized lubrication is “six fix”, “two clean”, “one sealing/leakage proof” and “three filtration”. Then an excellent lubrication center or oil depot management should be set up. We have the lubrication operation, carrying out equipment lubrication according to standard and schedule. Failure diagnosis through tear and wear status of the components is the extension of the system. It is necessary to recycle waste lubricating oil, it not only saves cost and oil resource, but also protects environment. Lubrication management informatization helps enterprise promote lubrication management level. Lubrication audit and improvement will make the system into an integrated close circle. A detailed description of the optimized lubrication management is given in this paper.
1. The procedure for Lubrication management
From the company’s point of view and high degree, there should be a procedure to normalize lubrication management. This procedure is the leading document to guide lubrication management in a company, equipment management department leads all workshops to implement lubrication management within this procedure. The main contents of a procedure should include: organization structure of lubrication management, lubricant selection, lubricant supply chain management, “six fix”, “two clean”, “one sealing/leakage proof”, “three filtrations”, lubrication center/depot management, lubrication operation, oil analysis and failure diagnosis, etc.
1.1 organization structure of lubrication management
Company designates someone to be responsible for lubrication management in equipment management department, workshop and each work team do the same as well. Take a company’s organization structure as an example, as shown in Figure 1.
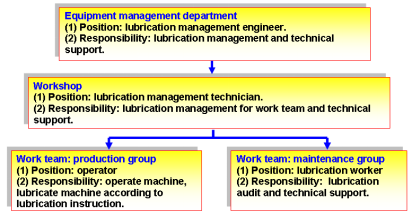
Fig.1.The organization structure of lubrication management
1.2 The choice of lubricant
There are some important factors we should consider to choose the lubricant. They are:
(1) Loading weight: this means that under what loading condition the friction pair is working, which will affect the lubricant choice;
(2) Moving speed: different speeds will need the different lubricant;
(3) Friction gap: different friction gaps will need the lubricant with different viscosities;
(4) Oil or grease characteristics: different characteristics of oil/grease are suitable to different working conditions, for example, in a fireproofing environment, inflaming retarding lubricant is necessary.
(5) Working temperature: even the temperature of different seasons will affect the lubrication status if we chose an improper lubricant. So, we should consider the working temperature, even the change of seasons while we chose the lubricant;
(6) Environment features: a dry or humid weather, a cold or hot region, a clean or dirty condition, all will affect the choice of the lubricant;
(7) Lubrication facilities: some lubrication is carried out by special devices such as oil-bath, oiling machine, etc. which is also affecting the choice of lubricant;
(8) Processing accuracy: for mechanical processing, the accuracy of product is emphasized, which will affect the choice of lubricant too.
The consideration factors for choosing the lubricant are shown by Fig. 2.
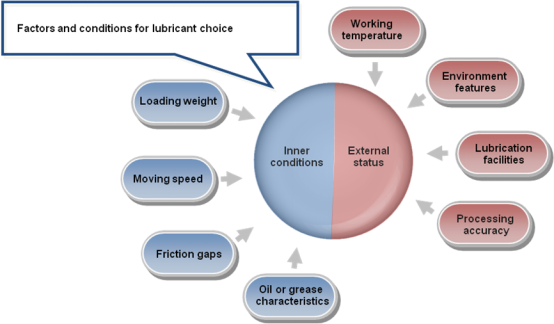
Fig. 2 .The consideration factors for choosing the lubricant
1.3 Lubricant Supply Chain Management
The lubrication supply chain management is related to planning, purchasing, acceptance checking, and receiving, delivering and recycling processes, which is shown by Fig.3.
1.4 The Core of Optimized Lubrication Management
What is the core of lubrication management? It is “six fix”, “two clean”, “one sealing/leakage proof”, and “three filtrations”.
“Six fix”: fixed oiling point, fixed operator, fixed oil quality, fixed oil quantity, fixed oiling method and fixed oiling period;
. “Two clean”: clean oiling tools, and clean oiling points;
“One sealing/ leakage proof”: to enhance the sealing and leakage prevention;
“Three filtrations”: filtrating when providing oil, filtrating when changing the container and filtrating when oiling.

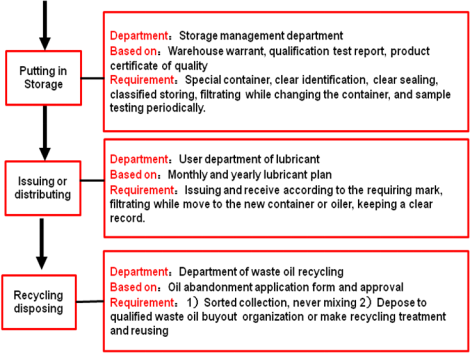
Fig. 3. The supply chain management of lubricant
(1) Content of “Six Fix”
So called “fix” is to confirm some important factors so as to make the lubrication executable. They are:
Fixed point: definite oiling position;
Fixed operator:Definite oiling people;
Fixed quality:Definite oil brand and quality;
Fixed quantity:Definite amount of oil;
Fixed method:Definite oiling way or method;
Fixed period:Definite oiling timetable.
(2) Two Clean Management
So called “Two cleans” means “clean oiling tools” and “clean oil inlet”. The aim of “Two clean” is the same with the “three filtration”. If the oil inlet or the oiling tools are dirty, then all abovementioned filtrations will be fail and useless.
(3) Sealing/Leakage Proof Management
Sealing and leakage proof management are also important within the lubrication management. In fact, generally, in a plant, a lot of oil is leaking away everyday, month by month, and year by year. It is not only a huge waste, but also affect the lubrication effect, cause an insufficient lubrication, then an excessive tear and wear, then the failure of equipment. Tab.1 shows the standard of leaking and seeping.
Tab.1 the Standard of Leakage or seepage.
Standard of Leakage or seepage | |
Definition | Status |
Seeping | Oil appears beyond 5 minutes after cleaning the surface |
Leakage | Oil appears within 5 minutes and forming the oil drop |
Seriously leaking | 3 drops of oil leaking within 1 minute, or 1kg oil leakage per day |
In general, the process of leakage prevention is as follows:
First we should set up a leakage standard, then make investigation to the status of oil leakage or seepage in accord with the standard, then look up the sources of leaking or seeping, then study and decide the method to solve the problem, such as changing, innovating, blocking, winding, welding, expanding, repairing, etc.
The concrete methods of leakage prevention are shown by Fig. 4.
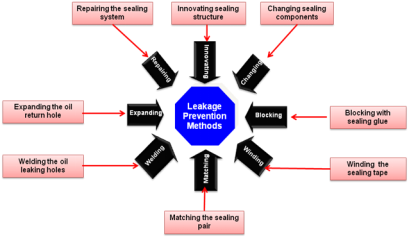
Fig. 4.The concrete methods of leakage prevention
(4) Three Filtration Management
“Three filtrations” mean that “oil supplying filtration”, “container changing filtration” and “oiling process filtration”. The aim of the three-filtration is to prevent the dust or production impurities get into the lubrication system, so as to prevent the decrease the effect of lubrication or the failure of the machinery.
1.5 Lubrication Center/Depot Management
Four things should be done to set up an excellent lubrication center or depot, which is shown by Fig. 5.
Fig.5. Lubrication Center/Depot Management
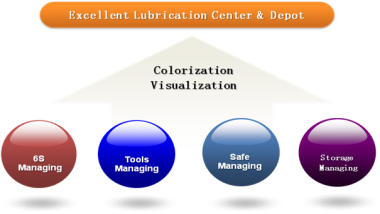
(1) 6S Managing
Housekeeping like 6S is especially necessary for lubrication center management. Fig.6 gives the lubrication center examples of 6S.


Fig.6. The excellent lubrication centers
(2) Tools Managing
The tools in the lubrication center such as oiling facilities, leaking oil receiver, oil pipe suspender, anti-freezing liquid injecting pump, heating circulation device, oil trolley, dustproof oil tank etc. should be well managed too.
(3) Safety Managing
The lubrication center or depot is a place with dangerous factors. The main principals of safety regulation of oil depot are as follows:
Inflammable and combustible material cannot be put around the oil depot;
Oil should be far away from steam pipeline, heat sources and the sources of radiation;
Fire protection and anti-explosion;
The electro-circuits and appliances should be inspected timely;
Keeping a clear road;
Anti-thunder, anti-static and anti-oil seep.
(4) Storage management
Regulations of Storage Management are:
Fixation and First in-first out (FIFO);
Perfect storage identification;
Keeping a ventilating, lighting, drying and dust –proofing environment;
Stored oil testing at a regular interval;
Complete in-storing-out procedure and periodic inventory;
Different locating of old and new oil;
Special-assigned person is responsible for the center or the depot.
Lubrication Operation
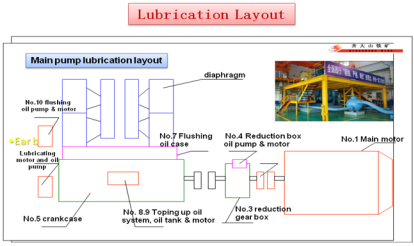
The key for optimized lubrication is the operation of lubrication, or to make the lubrication plan into practice, i.e. to operate lubrication according to the standard and schedule. In other words, the six fix, two clean, one sealing, and three filtrations be carried out completely. Fig.7 shows a visualized lubrication layout.
Fig.7. A lubrication layout in a plant
Oil Analysis and Failure Diagnosis
Working Principles of oil analysis and failure diagnosis are shown by Fig.8.
One aim of lubricant physical and chemical property index testing is to judge the quality of oil, another one is the failure diagnosis for the equipment.
Common physical and chemical property indices of lubricant are:
Chromaticity, viscosity, viscosity-thermal character, viscosity-press character, viscosity index, flash point, condensation point, pour point, moisture, mechanical impurity, residual carbon, ash content, ……etc..
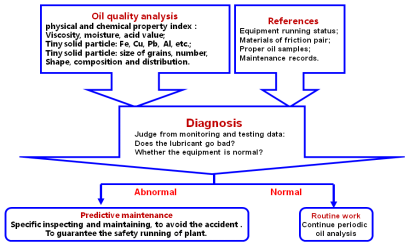
Common usability indices are:
Oxidation stability, thermal stability, oiliness, extreme pressure property, corrosion, air release property, form characteristic, demulsibility ……, etc..
Fig.8.Working Principles of oil analysis and failure diagnosis
The recycling of waste lubricating oil
The waste lubricating oil recycling is very important, which could not only save oil resources, but also protect the environment and prevent oil pollution. There are two basic approaches for handling waste lubricating oil: either you recycle it by yourself or you sell it to the qualified acquirer.
Recycling waste lubricating oil by yourself is one of the ways to save cost, it is not so difficult to recycle waste lubricating oil. Take a company’s recycling flowchart as an example, as shown in Figure 9.
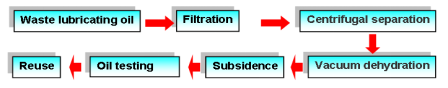
Fig.9. The flowchart of recycling waste lubricating oil
Lubrication management informatization
Many companies have already established lubrication management information system, it helps improve lubrication management level. Fig. 10 shows an example of framework of lubrication management information system.
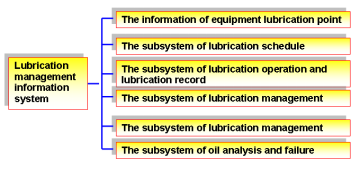
Fig. 10.Lubrication management information system
Lubrication Management Audit
We also give the general performance indices of lubrication audit shown as Fig. 11 which related to 10 aspects such as organization, technology, system, operation, information, etc.

Fig. 11. Performance indices of lubrication audit
Lubrication Improvement
There are two aspects to support the lubrication improvement, one is “One Point Lesson” which we call OPL, and another is “One Point Suggestion” which we call OPS. Since there are two “O”s, it is generally called “Aerobic Activities”. With aerobic activities, operators are implemented focusing to lubrication process, lubrication center/depot, lubricant supply chain, “six fix”, “two clean”, “one sealing/leakage proof”, “three filtration”, as well as lubricant and additive improvement continuously.
Conclusion
For a plant with many kinds of machineries, it is extremely important to have an excellent lubrication management. An optimized lubrication management should be a systematic design which relates to many aspects, from technology to management, from workshop to work team, from depot to recycling of waste lubricating oil, as well as the supply chain of lubricant. It is also a typical process of PDCA. The layout and framework of optimized lubrication management is shown by Fig. 12.
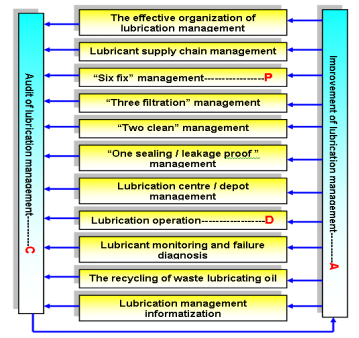
Fig. 12 Framework of optimized lubrication management
表单1
姓名*
*手机号*
*Email*
*其他联系方式*
*留言内容*
验证码
